Agile Energy X, TRIPLE-1, TEPCO Power Grid to implement distributed computing that hybridizes renewable energy and cutting-edge semiconductors
December 14, 2022
Agile Energy X, Inc.
TRIPLE-1, Inc.
TEPCO Power Grid, Inc.
Agile Energy X, Inc. (Henceforth: “Agile Energy X”) [100% subsidiary of TEPCO Power Grid, Incorporated], TRIPLE-1, Inc. (Henceforth: “TRIPLE-1”), which designs and develops advanced semiconductors and TEPCO Power Grid, Inc. (Henceforth: “TEPCO Power Grid”) has entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (“this MOU”) on November 11th, 2022 with the aim of establishing a robust and expansive strategic partnership based on the spirit and provisions of the “Basic Agreement on Exploring the Commercialization of the MW2MH(*1) Project.”
Under this MOU, Agile Energy X will contribute to the creation of a carbon-neutral society and the alleviation of power grid congestion through the development of distributed data centers throughout Japan that hybridize surplus power from renewable energy sources and TRIPLE-1’s cutting-edge semiconductors.

“Distributed computing” via a combination of “Renewable energy and cutting-edge semiconductors”
“Distributed computing” technology, which allows for the high-speed processing of vast amounts of digital data, will be key to making smart cities, automated driving, and the metaverse a reality in Japan’s society moving forward.
“Distributed computing” is an advanced technology in which numerous data centers (facilities that house IT equipment, including servers used for data processing) are set up throughout the country to carry out the arithmetic processing of large amounts of digital data, and by coupling them and operating them in parallel, these data centers function collectively as one massive computer system. “Distributed computing” is said to be an indispensable system for our next-generation digital society.
There is a need to develop these distributed data centers, which are located in a decentralized manner, especially in Japan due to its high frequency of natural disasters.
At the same time, along with the growing interest in environmental and energy-related issues around the world, equipping data centers with “energy-saving capabilities” has also become a major task. To this end, it is essential for us to take action to reduce power consumption, energy costs, and carbon dioxide emissions. In addition, there is a need to optimize the power grid as we attempt to make effective use of renewable energy for data center operations.
In view of this, Agile Energy X, TRIPLE-1 and TEPCO Power Grid have entered into this MOU with the aim of developing future distributed data centers that integrate “Tokyo Electric Power Company’s power transmission and distribution network” with the “surplus power generated from renewable energy sources nationwide” and “TRIPLE-1’s cutting-edge energy-saving semiconductors” under a project that will be spearheaded by Agile Energy X and deployed in various locations throughout Japan (hereinafter, “this Project”).
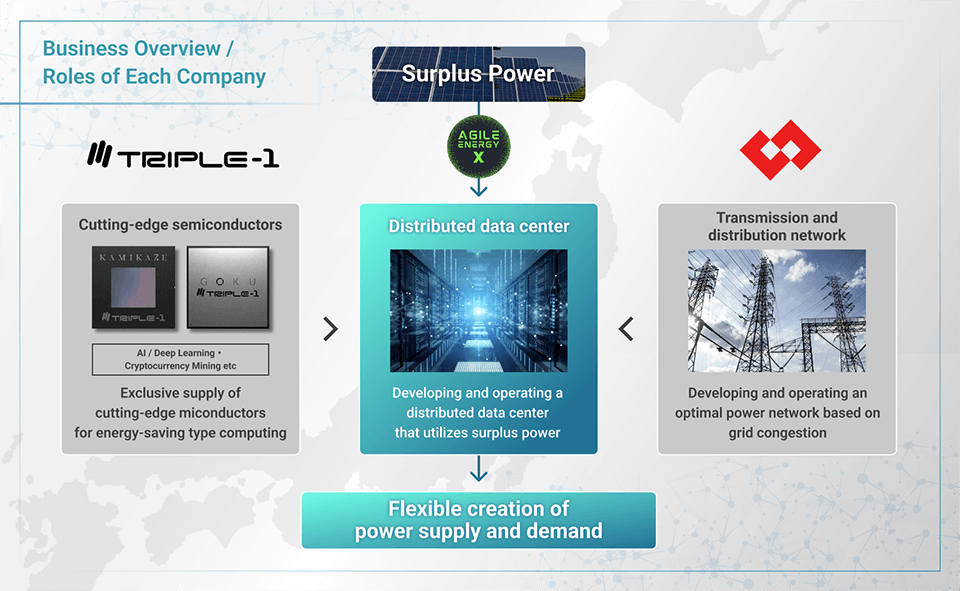
Making effective use of “surplus power” from renewable energy sources
The key point of this Project is that Agile Energy X will flexibly operate the distributed data centers by making effective use of the “surplus power” (*2) generated from renewable energy sources throughout Japan.
For instance, in the case of solar power, supply can easily exceed demand when power generation is concentrated on days with good weather, and the electric power generated cannot be used up. The amount of curtailment for such renewable energy sources has been rising nationwide in recent years, while it has also become difficult to interconnect renewable energy in some places due to power grid congestion. As a result, some national estimates (*3) suggest that Japan has the potential to generate up to twice the amount of electric power it currently generates by renewable energy.
The purpose of this Project is to make effective use of surplus power based on the concept of “local production for local consumption” by creating new demand for data centers and other facilities, rather than disposing of surplus power generated in excess of the existing demand or forcing the surplus power to flow into power lines and cause power grid congestion.
As a demonstration project for this Project, a data center with 1,300 computing systems (some of which are equipped with TRIPLE-1’s “KAMIKAZE”) has already been set up on the premises of TEPCO Power Grid’s business site in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Experiments aimed at exploring system behavior and the impact on the power grid when the facility is operated with a large amount of power on the scale of 1,500kW have begun to be conducted, with results showing that the facility can operate normally.
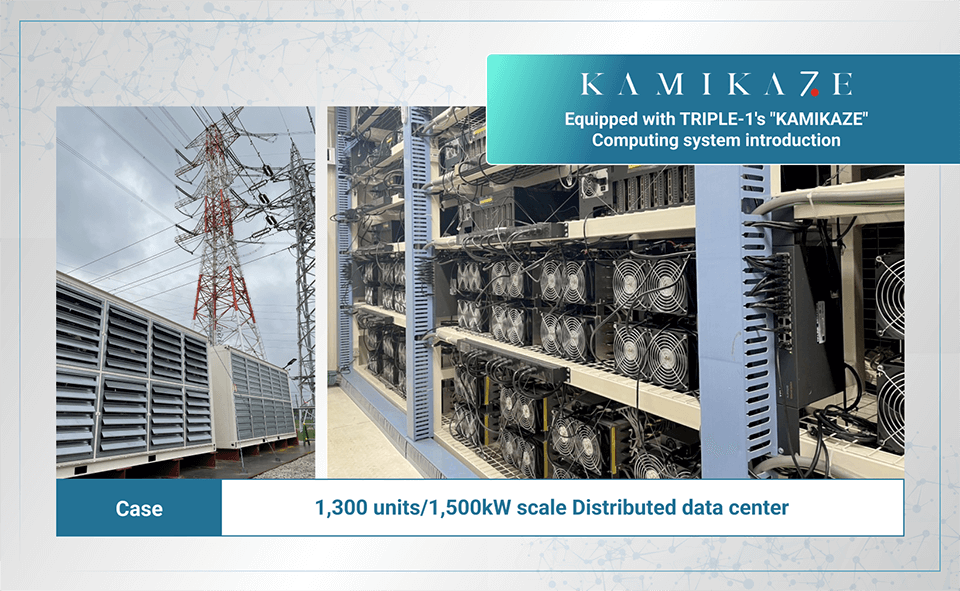
Semiconductors with extremely high power efficiency that utilize TRIPLE-1’s cutting-edge processing technology are used exclusively as computers in this Project. The selection and introduction of energy-saving products with a low environmental impact such as these constitute a vital initiative aimed at the creation of a carbon-neutral society.
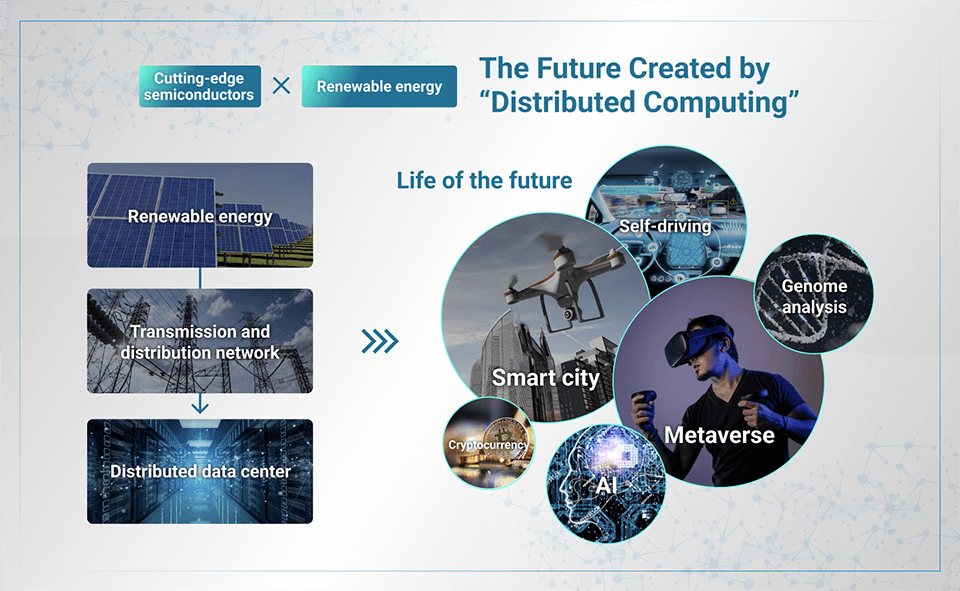
Toward its implementation in smart cities, automated driving, and the metaverse
Distributed computing is an important technology for facilitating next-generation technologies such as smart cities, automated driving, AI, 5G telecommunications, the metaverse, and cryptocurrency.
For instance, in order to make automated driving a reality, the AI must process in real time and at high speed not only the vehicle’s driving data but also large amounts of big data from the surrounding environment and other vehicles. This will be handled by distributed data centers that are based throughout the country. Moreover, CG rendering for running advanced graphics is necessary to reproduce a realistic world in the metaverse, a process that can also be handled by distributed data centers. Cryptocurrency mining and genome analysis are examples of other operations that can utilize these data centers.
The technology of distributed computing is expected to expand rapidly worldwide moving forward, with the global market size in 2028 estimated to be worth over US$56 billion (approximately 7.8 trillion yen) (*4).
In Japan, distributed computing powered by renewable energy is also expected to allow local governments to promote carbon-neutral (decarbonization) initiatives, support the growth of profits for renewable energy providers, facilitate the local production for local consumption of energy, as well as revitalize local economies.
Agile Energy X will work on this Project by taking advantage of its ability to procure materials such as TRIPLE-1’s cutting-edge semiconductors with the aim of establishing distributed data centers on the scale of 100MW in Japan by 2030.
(*1) MW2MH: Abbreviation for “MegaWatt To MegaHash,” which refers to the conversion of electric power (megawatt) into digital value (megahash)
(*2) Surplus power: Electric power that is wasted without being utilized in order to achieve a balance between power supply and demand or as a result of power grid congestion
(*3) Overview of section on introducing renewable energies in the Ministry of Environment’s “Japan’s Potential to Utilize Renewable Energy (tentative title)” report (in Japanese only)
https://www.renewable-energy-potential.env.go.jp/RenewableEnergy/doc/gaiyou3.pdf
(*4) Source: Global Information, Inc., Market Research Report
